A
AAMA
American Architectural Manufacturers Association. A national trade association that establishes voluntary standards for the window, door, and skylight industry.
Adjustable
Accessible without major reconstruction of the window, door, TDD, SSP, roof window, or unit skylight to bring the parts of the product to a true or more effective relative position.
Air Infiltration (Air-Leakage)
The amount of air leaking in and out of a building through cracks in walls, windows, and doors.
Air-Leakage Rating
A measure of the rate of air-leakage around a window or door in the presence of a specific pressure difference. The lower a window’s air-leakage rating, the better its airtightness.
Airspace
The space between adjacent layers in a multi-layer glazing system.
Ambient Temperature
The outdoor temperature.
Argon Gas
An inert, colorless, nontoxic gas used in insulating glass units to reduce heat transfer.
Astragal
A vertical member placed at the meeting edges of a double door to provide a weather seal and may be used to anchor the fixed door.
Awning Window
A window in which the sash is hinged at the top and opens by pivoting outward from the bottom using a crank handle.
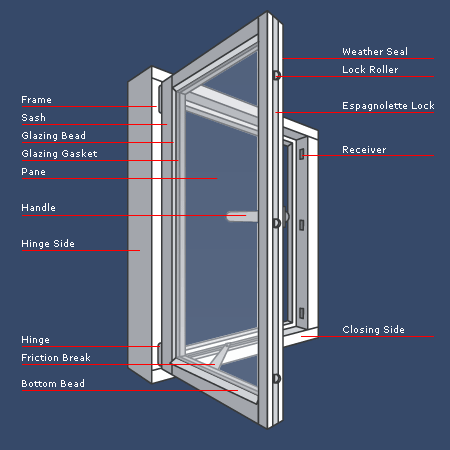
Window Terminology Diagram
B
Balance
A mechanism used in single and double hung windows as a means of counterbalancing the weight of the sash during opening and closing.
Basement window
Any window type intended for ventilating or illuminating a basement or cellar.
Bay Window
Traditionally made from three units with one large picture window flanked by two operating windows. The most popular combinations consist of double hung or casement style flanking windows. All the units can be stationary, operating, or any combination of the two.
Bite
The dimension by which the inner or outer edge of the frame or glazing stop overlaps the edge of the glazing.
Bottom Rail
The bottom horizontal part of a window sash.
Bow Window
Traditionally made of four or more windows joined together to form a delicate arch. A Bow can consist of any combination of windows.
Brickmold
A molding used as an exterior door or window casing.
British thermal unit (Btu)
The heat required to increase the temperature of 1 lb. of water 1°F.
Building envelope
The assembly or assemblies of materials and components that enclose building spaces and are exposed to exterior space or separate conditioned interior space from unconditioned interior space.
Butyl
A synthetic rubber used as a sealant and architectural glazing type.
C
Cable Support Kit
A hardware set designed to anchor a bay or bow window to a structure. The kit supports the projecting portion of the window and prevents sagging.
Call Size (Catalog Size)
A manufacturer’s reference number used to identify window and door dimensions.
Casement Window
A casement window is hinged on either side so the sash opens outward in a swinging motion to provide maximum ventilation.
Caulking
A compound for filling joints and sealing cracks to prevent leakage of water and air.
Cellulosic composite material
A composite material whose ingredients include cellulosic elements.
Certification
A process that indicates a representative sample of a product line has been tested, that the product meets specified requirements, and that the product is subject to ongoing inspections by an outside certification agency.
Check rail
See Meeting rail.
Chemically bonded (when related to a welded corner)
A process where the two polymer profiles or pieces are heated and fused together with the aid of a chemical reaction. The reaction and bonding is similar to the original extrusion process.
Cladding
See Fenestration cladding.
Closing force
See Operating force and Force to latch door.
Combination assembly
An assembly formed by a combination of two or more separate fenestration products whose frames are mulled together utilizing a combination mullion or reinforcing mullion.
Commercial entrance system
A system of products used for ingress, egress, and rescue generally in non-residential buildings.
Composite unit
A fenestration product consisting of two or more sash, leaves, lites, or sliding door panels within a single frame utilizing an integral mullion.
Concentrated load
A force applied to a fixed point on a window, door, TDD, SSP, roof window, or unit skylight component.
Condensation
A deposit of water vapor which occurs when excess humidity in warmer air is released as water droplets onto a colder surface.
Conduction
Heat transfer through a solid material, wherein heat flows from a higher-temperature area to a lower-temperature area.
Conditioned space
An area or room within a building that (a) is heated or cooled by any equipment or appliance; (b) contains uninsulated ducts; or (c) has a fixed opening directly into an adjacent area or room that is heated or cooled by any equipment or appliance or contains uninsulated ducts.
Corrosion
The deterioration of a material by chemical or electrochemical reaction resulting from exposure to weathering, moisture, chemicals, or other agents or media.
Cottage Window
This is a double-hung or single-hung window with an unequal top and bottom sash where the bottom sash is greater in height than the upper sash.
Crank Handle
Used in casement or awning windows, this handle has an arm and knob assembly.
Curtain wall
A non-load-bearing exterior wall cladding that is hung to the exterior of the building, usually spanning from floor to floor.
D
Deflection
Displacement due to flexure of a member under an applied load.
Design Pressure (DP) Rating
A method of specifying window performance which measures a product’s ability to withstand air and water forces, in negative and positive directions, while the window or door remains closed and locked.
Design wind load
The wind load pressure a product is required by the specifier to withstand in its end-use application.
Dew Point
The temperature at which the condensation of water vapor in a space begins, at a given state of humidity and pressure, as the temperature is reduced.
Divided Light (Divided Lite)
A window opening with a number of smaller panes of glass separated and held in place by a grid system.
Divider
A member that divides glazing into separate vision areas. Dividers are either structural or decorative. Other common terms are muntin, true divided lite (TDL), simulated divided lite (SDL), grill, grid, or bar-in-glass.
Dormer
An area that protrudes from the roof of a house, generally featuring one or more windows.
Double Glazing
Two pieces of glass separated by an air space to improve insulation against heat transfer where the air between the glass sheets is completely dried and the space is sealed airtight.
Double Hung Window
A window consisting of two sashes operating in a master frame where both the upper and lower halves slide vertically past each other and both tilt in for cleaning.
Dual-action window
A window consisting of a sash that tilts from the top and swings inward from the side for cleaning of the outside surface. Also referred to as a tilt-turn window.
Dual glazing
Two layers of glazing material mounted in a common frame and/or sash, separated by a space, and sealed or non-sealed.
Dual mode
The primary and secondary window/door, or both primary windows/doors, are closed, the primary windows/doors are locked, and the insect screen (when offered or specified by the manufacturer) is in the stored position.
Dual Pane
Two panes of glass with a single airspace, held together by an edge spacer – the most economical interglass unit.
E
Egress Hardware
Type of hinge used in casement windows which allows for a wider opening to meet emergency exit requirements.
Egress Opening
Space between the top of the sill of the master frame of an open window, the bottom part of a raised sash and the space between the jambs of the opening. Depending on location, the most popular requirement is a net clear opening of 20″ wide by 24″ high and not less than 5.7 square feet.
Egress Window
A window providing egress (the ability to leave an enclosed space. The minimum egress dimensions required by most building codes are 20” horizontally and 24” vertically.
Energy Star
Independent government program responsible for developing a standard set of guidelines designed to recognize the energy efficiency of various products including windows and doors.
Exterior Stop
The removable glazing bead that holds the glass or panel in place when it is on the exterior side of the lite or panel, as contrasted to an interior stop located on the interior side of the glass.
Extrusion
The process of producing vinyl or aluminum shapes by forcing heated material through a die. An item made by this process.
F
Factory Mulled
Two or more window units attached together at the manufacturing facility.
Fenestration
Openings in the building envelope, such as windows, doors, secondary storm products (SSPs) curtain walls, storefronts, roof windows, tubular daylighting devices (TDDs), sloped glazing, and skylights, designed to permit the passage of air, light, or people.
Fenestration cladding
The exterior components that cover the frame, sash, leaf, or sliding door panel members and constitute the weather-resistant surface.
Fixed Panel
The non-operating panel of a slider window or sliding door.
Fixed window
A window that is designed to be non-operable and consists of a glazed frame or a non-operating sash within a frame.
Flange
A flange can be a front-mounted fin on a window or dorwal. This facilitates its use in installation of stucco and replacement installation.
Float glass
Flat glass that has been formed on molten metal, commonly tin. The surface in contact with the tin is known as the tin surface or tin side. The top surface is known as the atmosphere side or air side.
Folding Crank Handle
Hardware with an arm and knob assembly where the handle folds down when not used. Common in casement windows.
Forced-entry resistance (FER)
The ability of a window or door in the locked position to resist entry under a specified load and conditions.
Force to latch door
The force required to close a door and fully engage the latch.
Frame
The head, jambs and sill that form an opening into which a sash or door panel fits. (see: Replacement Windows Reviews)
Full Screen
A screen which fills the entire window opening.
Fully tempered glass
Glass that has been heat treated to a high surface and/or edge compression to meet the requirements of ASTM C1048 (kind FT) or CAN/CGSB 12.1.
Fusion Welding
The process of joining vinyl window or door frames and/or sashes which entails the heating of each piece individually then joining them until bonded together. This eliminates water and air infiltration.
G
Garden Window
A box-shaped window with a slanted glass roof, typically with a glass shelf, which projects from the side of a structure and can be used as a miniature greenhouse.
Gateway performance requirements
The requirements for minimum gateway test size, air leakage resistance, structural design load and overload testing, water penetration testing, forced-entry resistance, and auxiliary testing which are the conditions permitting a product entry into a Performance Class.
Gateway test size
The minimum test specimen size specified to enter a Performance Class.
Glass
A hard, brittle substance, usually transparent, made by fusing materials such as soda ash (NA2CO3), limestone (CaCO3), and sand under high temperatures.
Glazing
The glass panes in a window, door, or skylight.
Glazing bead
Pieces of molding around the inside of a window sash or frame which hold the glass unit in place.
Grids
Decorative grids on the interior or exterior surface of the glass, between glass panes, or in any of these combinations which divides a glass unit into smaller openings to create any number of lites.
Grids Between The Glass (GBG)
A window or door option where grids are placed between panes of insulating glass.
Greenhouse window (aka garden window)
A window consisting of a three-dimensional, five-sided structure, with provisions made for supporting plants in the enclosed space outside the plane of the wall. Operating sash are allowed but are not required.
H
Half screen
A type of screen which covers only one half of the window, common in single and double hung as well as slider windows.
Handle
A component which enables the movement of a sash, leaf, or panel, or which activates a mechanism which locks or unlocks a sash, leaf, or panel.
Hardware
All the necessary equipment to retain, operate, and lock or unlock the sash, leaf, or panel within the frame.
Header (Head)
The upper horizontal part of a window frame.
Heat-strengthened glass
Glass that has been heat treated to a specific surface and/or edge compression range to meet the requirements of ASTM C1048 (kind HS).
Heat Gain
Transfer of heat from the outside to the inside of a structure through all surfaces.
Heat Loss
Transfer of heat from the inside of a structure to the outside through all surfaces.
High Performance (HP)
Products which have been tested to extra wind loads and water resistance test pressures enabling products to be used in installations which are subjected to environmental conditions which exceed the performance levels of a standard rated product.
Hinge
A device on which doors, windows, cabinets, etc. may turn or swing to open and close.
Hinged rescue window
Any window that is mounted into a stationary perimeter frame and is permanently hinged at one jamb.
Hopper Window
A window where the sash is hinged at the bottom and pulls inward for opening.
Horizontal Slider (Slider)
A window where one or both panels slide horizontally past each other.
Hung window
A window consisting of vertically sliding sash which utilize counterbalancing devices to allow the sash to be opened to any variable position between its fully open and fully closed limits.
I
ICC (International Code Council)
A national organization which publishes model codes for adoption by states and other agencies. Codes include the International Building Code (IBC) and the International Energy Conservation Code (IECC).
Infiltration (Air)
The movement of outdoor air into the interior of a building through cracks around windows and doors or in walls, roofs and floors.
Insulated Glass
Insulating glass refers to two or more pieces of glass spaced apart and hermetically sealed to form a single glazed unit with an air space between. Heat transmission through this type of glass may be as low as half that without such an air space.
Insulating Glass Unit
Two or more panes of glass spaced equally apart and hermetically sealed, forming a single glazed unit.
Insulation
Construction materials used for the protection from sound, heat, cold, or fire. A material with high resistance (high R-value or low U-value) that is used to retard heat flow. Air, Argon, or Krypton gas spaces between panes of glass provide insulation in IGUs.
Integral Nailing Fin
An integral nailing fin is part of the master frame of a New Construction window. It aids in the ease of installation as well as offering increased strength and stability.
Integral ventilating system/device
An apparatus that is independent from but installed into a window, door, or unit skylight product for the purpose of controlling the transfer of air through the window, door, or unit skylight product.
Interior accessory window (IAW)
A glazed frame and/or sash, attached inboard of existing prime windows, curtain wall, or storefront, in commercial buildings, to enhance control of thermal transmittance, solar heat gain, sound, air leakage, and/or daylight. IAWs are not intended for occupant operation or to be used with the exterior windows in the open position, nor are they intended to provide any specific resistance to air leakage or water penetration, or withstand structural load.
Interlock
An upright frame member of a panel in a window which engages with a corresponding member in an adjacent panel when the window is closed. An interlock on a window or door provides a hooking action between the sash rails reducing air infiltration and increasing security. (an overlap)
J
J-Channel
An optional extrusion part on a New Construction master frame which allows for a home’s siding to slip between the trim and nailing fin. It allows for easier installation since there is no need to finish the siding edge.
Jal-awning window
A window consisting of a multiplicity of top-hinged sash arranged in a vertical series within a common frame, each operated by its own control device which swings the bottom edges of the sash outward.
Jalousie window
A window consisting of a series of overlapping horizontal frameless louvers which pivot simultaneously in a common frame and are actuated by one or more operating devices so that the bottom edge of each louver swings outward and the top edge swings inward during operation.
Jamb
The vertical part at either side of a window frame or the horizontal part at the top of the window frame.
Jamb Depth
Width of a window or door from the interior to the exterior of the frame.
Jamb Extension
Wood, most commonly, attached to the inside edges of the window or door to extend its width and adapt it to a thicker wall.
K
Keeper
A bracket employed as a latching point in locking hardware.
Knocked-Down
Describing the final product as unassembled, most commonly a patio door.
Krypton Gas
An inert, odorless, nontoxic gas used in insulating windows to reduce heat transfer. Less common and more expensive than Argon Gas.
L
Laminated Glass
Two or more panes of glass bonded together with a layer of plastic in between.
Leaf
A part of a side-hinged door system, glazed or unglazed, surrounded by a frame. Leaves can be fixed in place (non-operable) or movable (operable).
Lift Rail
The bottom part of the sash on a double or single hung window designed with an integrated method of lifting the operating sash.
Light (Lite)
When glass in a window or door is divided by a grid into multiple smaller openings, those openings are called lites.
Limited water (LW) (as a designation)
That the water penetration resistance performance is achieved by testing at a pressure less than the minimum test pressure required for the indicated Performance Class and Performance Grade (PG).
Lintel
A horizontal beam above a window or door opening which supports the weight of the wall above the opening.
Lock
The device on a window or door that secures it in a closed position.
Louver
A slatted opening for ventilation in which the slats are so placed to exclude rain, sunlight, or vision.
Low-Emittance Coating (Low-E)
Microscopically thin, virtually invisible, metal or metallic oxide layers deposited on a glazing surface primarily to block harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays and the sun’s infrared heat. Homes with Low-E glass stay cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter.
M
Manufacturer
A company which fabricates and/or assembles one or more parts, components, and/or accessories or supplies entire fenestration systems.
Mechanical Window
A window in which the corners are assembled using screws as opposed to a welded corner construction.
Meeting Rail
The part of a window or sliding door where two panels meet.
Meeting stile
One of the two adjacent vertical leaf, sash, or panel members that come together when in the closed position.
Minimum gateway test size
The test specimen size specified to enter a Performance Class at the lowest or minimum level.
Moisture content
The percentage of dry weight that is composed of water, such as in wood.
Mullion
A part used to structurally join two or more window or door units.
Mulled Unit
Two or more window or door units joined together.
Multiple glazing panel (MGP)
A glazed panel that can be installed in or on a sash, leaf, or panel on either the interior side or exterior side of the primary glazing. An MGP is tested only in conjunction with a specific primary window or door.
Multipoint Locking System
A locking system where there is more than one locking point.
N
Nailing Fin (Nailing Flange)
An integral part of a New Construction window or patio door master frame which usually overlaps the stud and through which nails are driven to secure the frame in the opening.
National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC)
The NFRC is an independent third-party certification organization with industry-accepted standards for evaluating and certifying energy performance. The NFRC Certificate contains U-factor, SHGC (Solar Heat Gain Coefficient), and VT (Visible Transmittance) values. These values form the basis for the ENERGY STAR Door and Window Program.
Negative pressure
Pressure acting in the outward direction.
Non-hung window
A window consisting of vertically sliding sash which utilize mechanical retainers or slide bolts to allow the sash to be opened to any one of the pre-selected positions between its fully open and fully closed limits.
Non-operable
Intended to not open or close.
O
Obscure Glass
Any textured glass, usually frosted, used for privacy while still allowing light to penetrate.
Operable Window
Any type of window which can be opened for ventilation.
Operator
Crank-operated hardware used in opening and closing casement windows.
Operating force
The force required to initiate or maintain a sash, leaf, or panel motion in either the opening or closing direction.
Oriel Window
This is a double or single hung window with an unequal top and bottom sash where the top sash is greater in height than the lower sash.
Outdoor-indoor transmission class (OITC)
A single-number rating calculated in accordance with ASTM E1332, using values of outdoor-indoor transmission loss, that provides an estimate of the sound insulation performance of a facade or building elements.
Overall dimensions
The external height and width of the product, expressed in millimeters or inches.
P
Pane
A single sheet of glass.
Panel
The component of a sliding glass door, consisting of a glass unit in a frame installed within the master frame of the door. May be stationary or active.
Parallel opening window
A window consisting of an operable sash that moves outward in a horizontal direction perpendicular to the plane of the frame for the purpose of ventilation. The sash remains parallel to the frame throughout its range of motion.
Performance Class
One of the five Performance Classes (R, LC, CW, AW, and SK) within the classification system that provides for several levels of performance.
Performance Grade (Grade or PG)
A numeric designator that defines the performance of a product in accordance with this Standard/Specification.
Picture Window
A fixed window which does not open for ventilation.
Pivot
An axis or the hardware about which a window, sash, panel, or leaf rotates.
Pivoted window
A window consisting of a sash which pivots about an axis within the frame. The pivoting action of the window allows for easy access to clean the outside surfaces of the window. Two common types are the 180° compression seal pivoting window and the 360° pivoting window.
Plastic glazing
Plastic infill materials (including, but not limited to, acrylic, co-polyester, fiberglass-reinforced plastic, and polycarbonate) that are glazed or set in a frame or sash.
Positive pressure
Pressure acting in the inward direction.
Primary window
That window in a dual-window unit so designated by the manufacturer, capable of protecting the building’s interior from climatic elements (as opposed to a secondary window used mainly for performance enhancement).
R
R-Value
A measure of the resistance to heat flow. A window with a high R-value has a greater resistance to heat flow and a higher insulating value.
Rail
Horizontal part of a window sash.
Reinforcement
The material added to individual sash, leaf, panel, or frame members to increase strength and/or stiffness.
Retrofitting
Adding or replacing items on existing structures.
Revolving door
An exterior door consisting of two or more leaves that pivot about a common vertical axis within a cylindrically shaped vestibule.
Roof window
A sloped application of a fenestration product that provides for in-reach operation.
Rough Opening
The opening in a wall into which a door or window is to be installed.
S
Safety glass
A strengthened or reinforced glass that is less subject to breakage or splintering, such as glass for doors, unit skylights, and some windows.
Sash
The part of a window which includes the glass unit and the frame sections directly attached to it.
Screen
Woven metal, plastic, or fiberglass mesh stretched over a frame which sits inside the master frame of the window or door and permits air to pass through while stopping insects.
Seal Failure
Loss of the airtight seal in the insulated glass unit which results in fogging between the glass panes.
Sealant
A compound used to fill and seal a joint or opening.
Seat Board
A board cut to fit the contour of a Bay or Bow window which provides a seat or shelf space.
Secondary door
That door in a dual-door system so designated by the manufacturer, used on the exterior of, or interior of, and in tandem with, a primary door designated by the manufacturer to be used for the purpose of performance enhancement, and not to be used by itself as a primary door.
Secondary storm product (SSP)
A door, window, or skylight product intended to be used only in conjunction with a primary door, window, or skylight product for the purpose of enhancement of performance in a system with the primary product. A secondary storm product can be attached to the internal or external frame or sash of the primary product. A secondary storm product is also considered a secondary door or window.
Secondary window
That window in a dual-window unit so designated by the manufacturer, used on the exterior of, or interior of, and in tandem with, a primary window for the purpose of performance enhancement, and not to be used by itself as a primary window.
Serviceable
Accessible without major reconstruction of the window, door, SSP, TDD, roof window, or unit skylight.
Setting block
A device or member that supports the weight of the glazing and is in direct contact with an edge of the glazing after final installation.
Side-hinged door system
A door system having, at a minimum, a hinge attachment of any type between a leaf and jamb, mullion, or edge of another leaf but having a single, fixed vertical axis about which the leaf rotates between open and closed positions. These systems include, at a minimum, a single operating leaf, surrounding frame, and components. The surrounding frame has vertical and horizontal members that are joined at the intersections and fully encompass the operating and/or fixed leaf/leaves.
Side-hinged (inswinging) window
A window that consists of sash hinged at the jambs that swings inward using exposed butt hinges or concealed butt hinges, and in some cases friction hinges. It is used primarily for cleaning or emergency escape and rescue purposes, but not for ventilation other than in the case of emergency. The gateway test size is larger than for casement windows, but otherwise the same requirements are met. See also Hinged rescue window and Top-hinged window.
Side lite
An operable or non-operable product that is designed to be a companion product installed on one or both sides of an operable door or a fixed door. Side lites often have their own separate frame or are contained within the frame of a composite assembly.
Sill
The lowest horizontal part of a window or door frame.
Simulated Divided Lights (SDL)
A window or door unit with the grilles placed between and on the glass surface which has the appearance of a number of smaller panes of glass in one frame.
Single Glazing
A single pane of glass in a window or door.
Single-Hung Window
A window consisting of two sashes where the upper sash is fixed and the bottom sash moves up and down as well as tilts in for cleaning.
Single-Strength Glass
Glass with a thickness between 0.085″ and 0.100″ (2.16¬2.57 mm).
Single mode
The primary window/door is closed and latched, the secondary window/door or outer primary window/door is opened fully, and the insect screen (when offered or specified by the manufacturer) is in the functional position.
Skylight
A roof window which gives light and, if it is operable, ventilation.
Slider Window
A window consisting of two or more sashes which operate by sliding horizontally past each other.
Sliding Glass Door (Patio Door)
A door consisting of two or more panels which move horizontally on a track. Usually only one of the panels is active and moves in a rolling rather than sliding motion.
Sloped glazing (other than unit skylights)
A glass and framing assembly that is sloped more than 15° from the vertical and which forms essentially the entire roof of the structure.
Sound transmission class (STC)
A single-number rating calculated in accordance with ASTM E413, using sound transmission loss values, that provides an estimate of the sound insulation performance of an interior partition in certain common sound insulation problems.
Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC)
The measurement of solar radiation emitted through a window expressed as a number between 0 and 1. The lower a window’s solar heat gain coefficient, the less solar heat it transmits.
Spacer
A material which separates the panes of glass to create the airspace in an insulating glass unit.
Span
The clear distance measured parallel to the length of a mullion or divider between support points.
Spandrel
The opaque areas of a building envelope which typically occur at locations of floor slabs, columns, and immediately below roof areas.
Specification
A written document often accompanying architectural drawings, giving such details as scope of work, materials to be used, installation method, required performance, and quality of work for work under contract.
Stile
A vertical member of a sash, leaf, or panel.
Stress Crack
A defect resulting from a stress condition originating at a point along any of the edges of a piece of glass.
Structural test pressure (STP)
The pressure differential applied to a window, door system, TDD, roof window, SSP, or unit skylight.
Sunroom
A multi-sided structure consisting of a high percentage of glazed area versus framing area.
System
The parts, components, hardware, and/or accessories that yield a complete, fully functional assembly.
T
Tempered Glass
Glass which is strengthened by reheating it to just below the melting point and then suddenly cooling it. This process gives it the ability to break into small pieces when shattered making it ideal for safety glazing in patio and entry doors, side lights, and other hazardous locations.
Test specimen
A complete, fully functioning window, door, SSP, TDD, roof window, or unit skylight supplied by the applicant and fitted in the test apparatus in accordance with the manufacturer’s written installation instructions (including the manufacturer’s instructions for clearance, shimming, and anchoring).
Thermal Break
A barrier between elements of high conductance which reduces the flow of heat. This is often used in aluminum windows.
Thermal Expansion
A dimensional change in a material due to temperature changes.
Thermoplastic
A polymer material that turns to liquid when heated and becomes solid when cooled and is able to repeat these processes.
Tilt Latch
Mechanism at the top of each sash which allows for inward movement for cleaning as well as removal purposes.
Tinted Glass
Glass colored in the manufacturing process by the addition of a mineral admixture.
Top-hinged window
A window consisting of sash hinged at the head which swings inward or outward using a continuous top hinge or individual hinges, primarily for cleaning or emergency escape and rescue purposes and not for ventilation.
Torsion
The twist induced in a product by the application of a static load to an extreme free corner of that product and normal to its plane.
Transom
A window above a door or another window, usually non-operable.
Tributary width
The width of wind-bearing area contributing to the load on a mullion or divider.
Triple Glazing
Three pieces of glass separated by two air spaces to improve insulation against heat transfer where the air between the glass sheets is completely dried and the space is sealed airtight.
Tropical awning window
A window consisting of one or more top-hinged or pivoted sash that swing outward at the bottom edge and are operated by one control device that securely closes them at both jambs without the use of any additional manually controlled locking devices.
True Divided Lite
A window opening comprised of multiple individual smaller panes of glass separated by grilles.
Tubular daylighting device (TDD)
A non-operable fenestration unit primarily designed to transmit daylight from a roof surface to an interior space via a closed-end tubular conduit. The basic unit generally consists of an exterior glazed weathering surface, a light-transmitting tube with a reflective inner surface, and an interior closure glazing in a retainer frame. The interior closure glazing is generally sealed. A TDD product line can be tested and rated in either or both of the following configurations: (a) Closed ceiling (CC): the tubular conduit passes through unconditioned space. (b) Open ceiling (OC): the tubular conduit is suspended in conditioned space.
U
U-Value (U-Factor)
A measure of the rate of heat loss through a window or door. The lower the U-value, the greater a window’s resistance to heat flow and the better its insulating value.
Ultraviolet Light (UV)
Invisible rays of solar radiation at the short-wavelength violet end of the spectrum. UV rays can cause fading of paint finished carpets and fabrics, as well as deterioration of some materials.
Unit skylight
A complete factory-assembled glass- or plastic-glazed fenestration unit consisting of not more than one panel of glass or plastic installed in a sloped or horizontal orientation primarily for natural daylighting. Unit skylights are either fixed (non-operable) or venting (operable).
V
V-Groove
A decorative pattern which is “grooved” into the glass using a special process.
Vehicular-access door
A door that is used for vehicular traffic at entrances of buildings such as garages, loading docks, parking lots, factories, and industrial plants, and is not generally used for pedestrian traffic.
Veneer
A thin sheet or layer of wood.
Vertical fenestration
Fenestration products that are installed at an angle less than 15° from vertical.
Vertical sliding window
A hung or non-hung window consisting of at least one manually operated sash that slides vertically within a common frame.
Vinyl
Polyvinylchloride (PVC) material that can be both rigid or flexible, used in glazing channels and weathering of both windows and doors. (see vinyl windows)
Vinyl Glazing
Holds glass in place with extruded vinyl channels or roll-in type application.
Virgin Extrusion
Extrusions which are produced from virgin vinyl with no regrind added.
Visible Transmittance (VT)
The percentage of available light which comes through a window. The higher the VT, the more daylight comes in.
W
Warm-Edge Technology
Use of low-conductance spacer materials to reduce heat transfer near the edges of insulated glass units.
Warping
What happens when an object is twisted out of shape.
Water penetration
Penetration of water beyond the plane intersecting the innermost projection of the test specimen, not including interior trim and hardware, under the specified conditions of air pressure difference across the specimen.
Weatherstripping
Variously shaped material which covers the joints between the sashes and master frame reducing air and water infiltration.
Weep Hole
A small opening in a window or door sill through which water may drain to the building exterior.
Welded
When materials are fused by heat to become one when cooled.
Window
An operable or non-operable assembly that is installed in an opening within an exterior wall or roof intended to admit light or air to an enclosure, and is usually framed and glazed.
Window wall
A non-load-bearing fenestration system provided in combination assemblies and composite units, including transparent vision panels and/or opaque glass or metal panels, which span from the top of a floor slab to the underside of the next higher floor slab.
Note: Window walls are available with separate or integral slab edge covers and can be fabricated from windows or curtain wall or storefront systems. Primary provision for anchorage occurs at head and sill conditions. Receptor systems can be designed as a part of drainage and movement accommodation provisions.
Window & Door Manufacturers Association (WDMA)
The Window & Door Manufacturers Association defines the standards of excellence in the residential and commercial window, door and skylight industry and advances these standards among industry members while providing resources, education and professional programs designed to advance industry businesses and provide greater value for their customers. (see WDMA.com)